How to Deploy RabbitMQ – Message Broker System
How to Deploy RabbitMQ – Message Broker System
Deploy RabbitMQ with Docker Compose on Ubuntu 24.04 using Traefik for secure management UI.
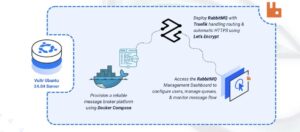
RabbitMQ is a lightweight message broker that enables applications to communicate asynchronously by sending messages through queues instead of interacting directly. This architecture improves reliability, scalability, and performance across distributed systems.
This article explains how to deploy RabbitMQ using Docker Compose, configure persistent storage for queue data, and secure the RabbitMQ Management UI using Traefik with HTTPS routing.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have:
- Access to an Ubuntu 24.04-based server as a non-root user with
sudoprivileges. - Installed Docker and Docker Compose.
- Created a DNS A record pointing to your server’s IP address (for example,
rabbitmq.example.com).
Set Up the Directory Structure and Environment Variables
In this section, you create a project directory for RabbitMQ and define environment variables in a .env file that Docker Compose loads automatically.
- Create the project directory.
console
$ mkdir -p ~/rabbitmq-stack - Navigate in to the project directory.
console
$ cd ~/rabbitmq-stack
- Create a
.envfile to store the environment variables.console$ nano .envAdd the following variables:
iniDOMAIN=rabbitmq.example.com LETSENCRYPT_EMAIL=admin@example.com RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=admin RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=STRONG_PASSWORD
Replace:
rabbitmq.example.comwith your domain.admin@example.comwith your email.STRONG_PASSWORDwith a secure alphanumeric password.
Save and close the file.
Deploy with Docker Compose
In this section, you create the Docker Compose manifest that deploys RabbitMQ and Traefik. Docker Compose uses the .env file to inject variables for domain routing, certificate generation, and default RabbitMQ credentials.
- Create the Docker Compose manifest.
console
$ nano docker-compose.yamlAdd the following content:
yamlservices: traefik: image: traefik:v3.6 container_name: traefik command: - "--providers.docker=true" - "--providers.docker.exposedbydefault=false" - "--entrypoints.web.address=:80" - "--entrypoints.websecure.address=:443" - "--entrypoints.web.http.redirections.entrypoint.to=websecure" - "--entrypoints.web.http.redirections.entrypoint.scheme=https" - "--certificatesresolvers.letsencrypt.acme.httpchallenge=true" - "--certificatesresolvers.letsencrypt.acme.httpchallenge.entrypoint=web" - "--certificatesresolvers.letsencrypt.acme.email=${LETSENCRYPT_EMAIL}" - "--certificatesresolvers.letsencrypt.acme.storage=/letsencrypt/acme.json" ports: - "80:80" - "443:443" volumes: - "letsencrypt:/letsencrypt" - "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro" restart: unless-stopped rabbitmq: image: rabbitmq:4.2-management container_name: rabbitmq hostname: rabbitmq environment: - RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=${RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER} - RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=${RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS} ports: - "5672:5672" expose: - "15672" volumes: - "rabbitmq-lib:/var/lib/rabbitmq" - "rabbitmq-log:/var/log/rabbitmq" labels: - "traefik.enable=true" - "traefik.http.routers.rabbitmq.rule=Host(`${DOMAIN}`)" - "traefik.http.routers.rabbitmq.entrypoints=websecure" - "traefik.http.routers.rabbitmq.tls.certresolver=letsencrypt" - "traefik.http.services.rabbitmq.loadbalancer.server.port=15672" restart: unless-stopped volumes: letsencrypt: rabbitmq-lib: rabbitmq-log:
Save and close the file.
In this manifest:
- services: Defines the containers managed by Docker Compose:
- traefik: Acts as the reverse proxy, handles HTTPS termination, manages routing, and automatically generates Let’s Encrypt certificates.
- rabbitmq: Runs the RabbitMQ server and exposes the Management UI.
- image: Specifies the container image used for each service.
- container_name: Assigns a fixed container name to simplify logging and container management.
- command (Traefik): Configures Traefik with Docker service discovery, HTTP/HTTPS entry points, automatic HTTP→HTTPS redirection, and ACME (Let’s Encrypt) certificate generation.
- ports (Traefik): Publishes ports
80and443on the host so Traefik can receive and route all incoming traffic. - ports (RabbitMQ): Maps port
5672, the primary AMQP messaging port, to the host. - expose (RabbitMQ): Exposes port
15672(RabbitMQ Management UI) to Traefik internally without exposing it directly to the host machine. - volumes:
rabbitmq-libstores RabbitMQ’s persistent message/queue data.rabbitmq-logstores RabbitMQ log files.letsencryptstores TLS certificates generated by Traefik./var/run/docker.sockallows Traefik to detect running Docker services automatically.
- labels (RabbitMQ): Enables Traefik for the container, defines the domain-based routing rule, selects the HTTPS entry point, and specifies the internal port (
15672) Traefik should forward requests to. - restart: unless-stopped: Ensures the service automatically restarts unless manually stopped.
- services: Defines the containers managed by Docker Compose:
- Start the services.
console
$ docker compose up -d - Verify that both services are running.
console
$ docker compose psOutput:
NAME IMAGE COMMAND SERVICE CREATED STATUS PORTS rabbitmq rabbitmq:4.2-management "docker-entrypoint.s…" rabbitmq 2 hours ago Up 2 hours 4369/tcp, 5671/tcp, ... traefik traefik:v3.6 "/entrypoint.sh --pr…" traefik 2 hours ago Up 2 hours 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:443->443/tcp, ...The above output confirms that both services are running successfully.
- View the logs for the services.
console
$ docker compose logsFor more information on managing a Docker Compose stack, see the How To Use Docker Compose article.
Access the RabbitMQ Management Dashboard
In this section, you open the RabbitMQ Management UI using the domain you configured and verify that the dashboard loads correctly.
- Open the RabbitMQ Management Dashboard in your browser.
https://rabbitmq.example.com - Log in using the credentials you configured in your
.envfile. - After successful authentication, the RabbitMQ Management Dashboard appears.
Conclusion
You have successfully deployed RabbitMQ with the Management UI using Docker Compose and Traefik. Traefik handled HTTPS and routing for the management dashboard, and RabbitMQ stored data and logs on persistent host volumes. You can now create admin users, manage queues via the dashboard, and connect applications to RabbitMQ on port 5672.